Primary Structure of DNA
The sequence of nucleotide chains is the primary structure of DNA. The genetic information is stored in these channels, and while the skeleton is the same for everyone, the variation in information is found in the varied sequence of nitrogenous bases. This sequence includes a code that specifies the order of the bases or other information.
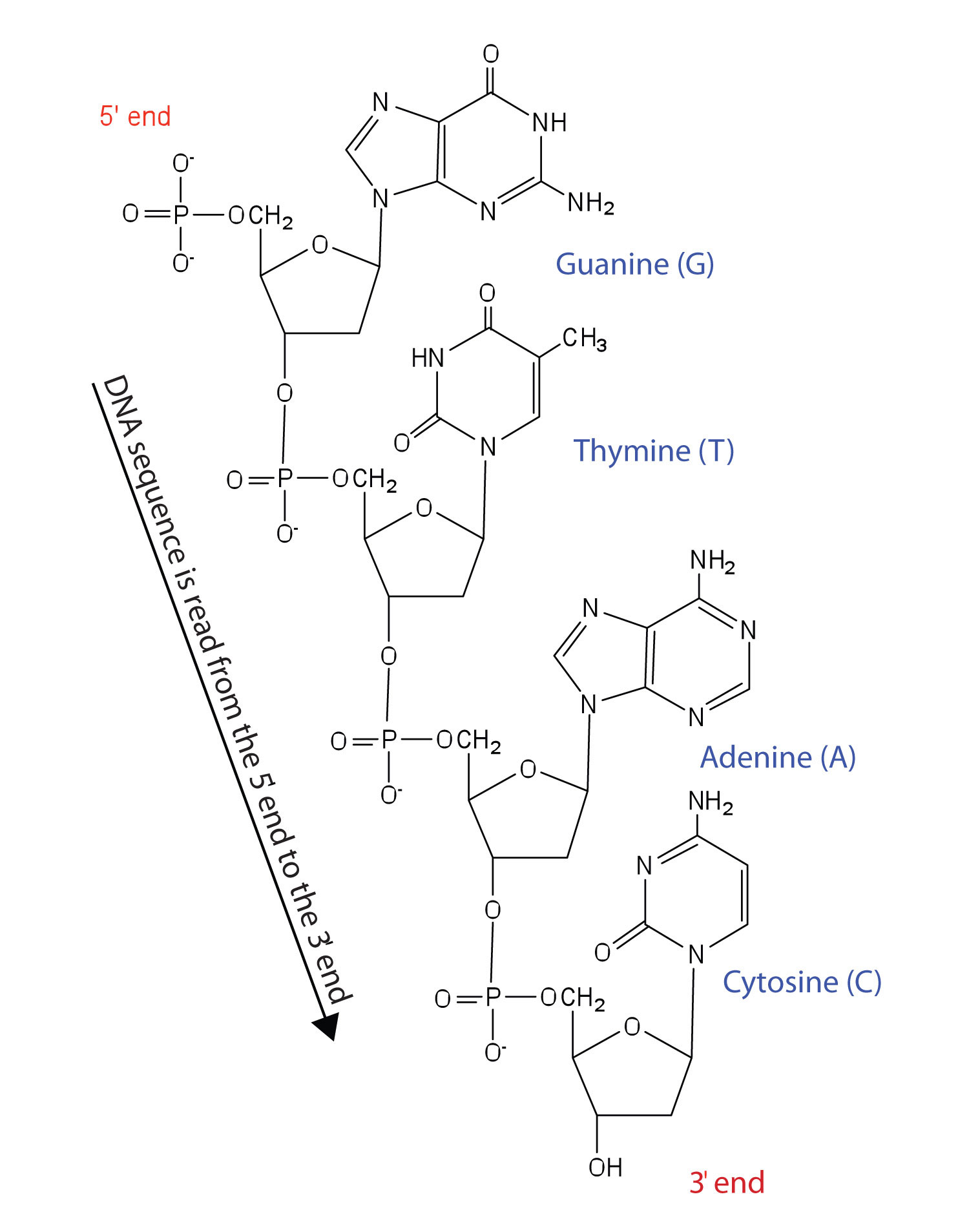
Secondary Structure of DNA
It is a double helical structure. The secondary structure of DNA helps explain how genetic information is stored and how DNA replication works. Based on X-ray diffraction experiments by Franklin and Wilkins and the Chargaff equivalence of bases, Watson and Crick proposed that the total of adenines and guanines is equal to the sum of thymines and cytokines.
Depending on the DNA, it is a double strand that is either right-handed or left-handed. Both chains are complementary because adenine and guanine in one chain are connected by thymine and cytosine in the other. Because both chains are antiparallel, the 3′ end of one faces the 5′ end of the other.
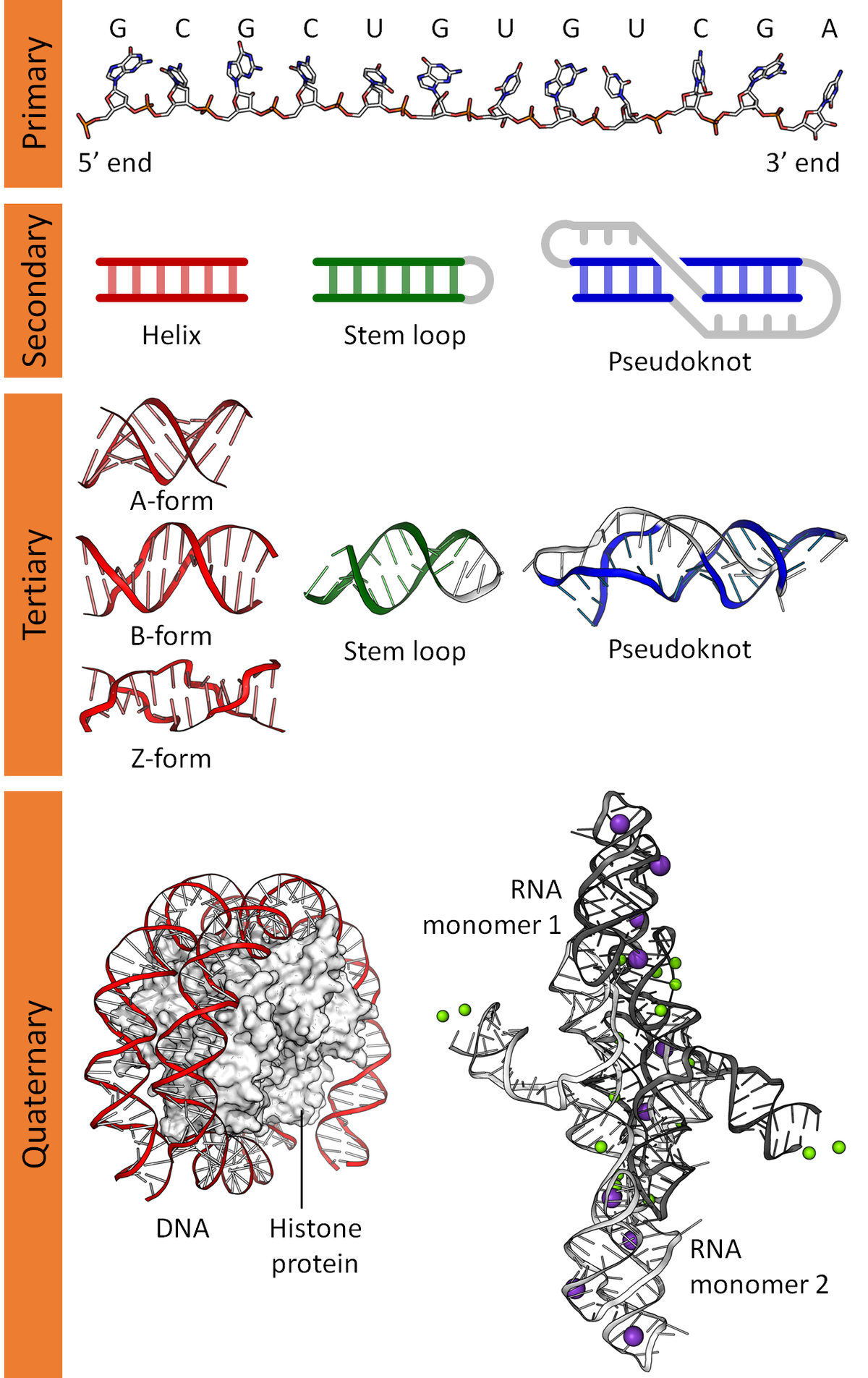
Read more on the Structure of Nucleic Acids and DNA

Post a Comment